You like Google Trends but you’re disappointed that it doesn’t work well for long tail keywords? Then keep on reading and use this python script to build your own “Google Trends” service by using the Google Autosuggest.

The official Google Trends service is highly appreciated for analyzing new search behavior. However, there are two things that stopped us from using it for more than “just playing around”:
- If your focus are finding new niche keywords, Google Trends doesn’t show you sufficient data.
- There is no official API for making requests to Google Trends, if you use modules like pytrends, you have to use proxy servers to avoid getting blocked.
In short: This won’t solve the job for detecting new niche keywords on scale. Let’s build a solution in python that is doing the job.
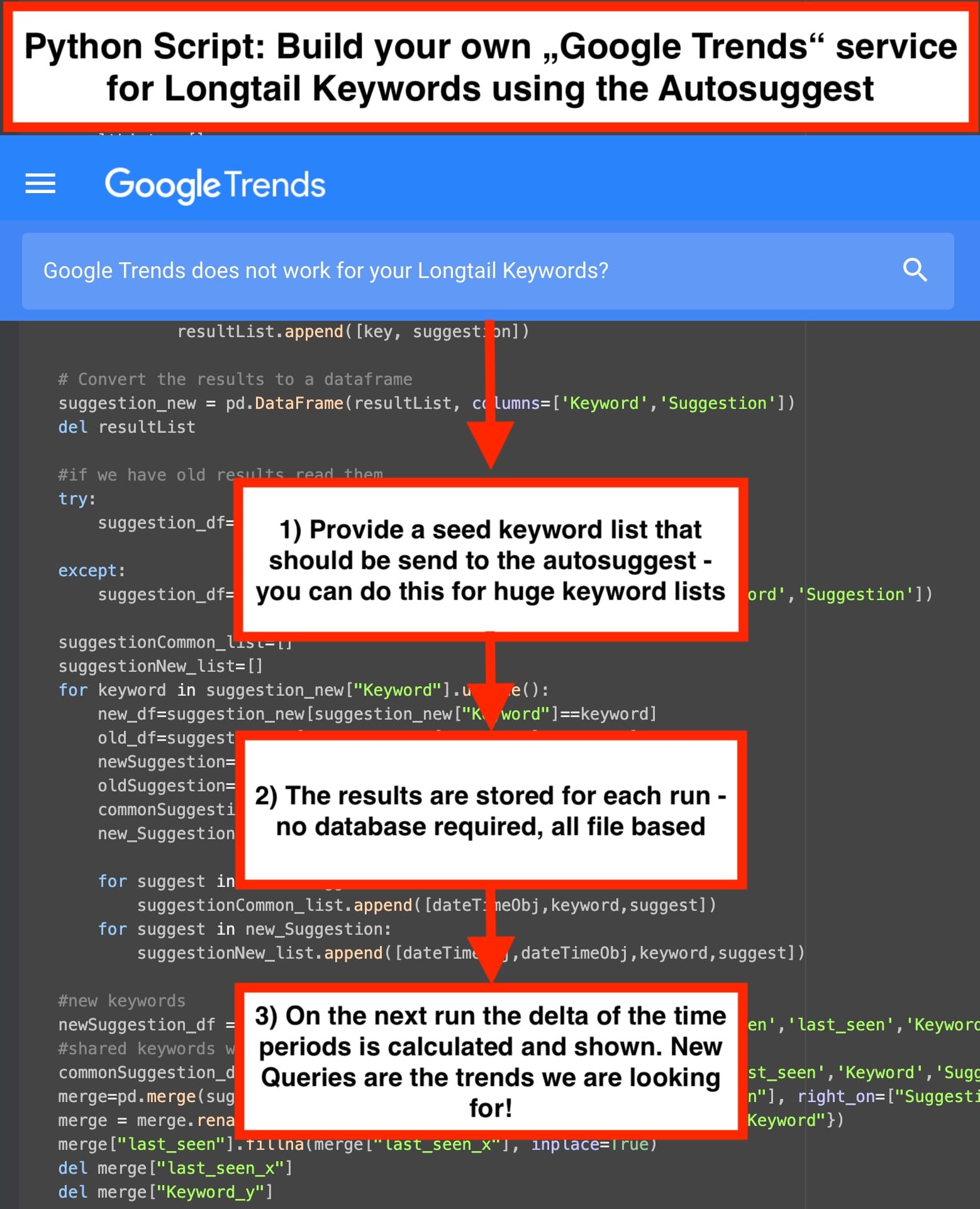
Fetch and store autosuggest results over time and look at the changes
Let’s say you have 1000 seed keywords you send to the Autosuggest. This will give you probably around 200.000 longtail queries. Then do the same one week later and compare both data sets:
- Which Queries are new compared to your last run? This is probably the case you are interested in. Google thinks those queries are getting more important—this is how you can build your custom Google Trends solution.
- Which Queries aren’t visible anymore?
The Python Script is very straight forward and most of the code we already shared here. The new part is about saving the data from past runs and make the comparison between the suggestions over time. We avoided to use file based databases like SQLite for simplicity—so all the data storage is done using CSV Files. Just import the file in Excel and explore niche keyword trends for your business.
Please follow these steps:
- Enter your seed keyword set that should be send to the autocomplete: keywords.csv
- Adjust the Script settings for your need:
- LANGUAGE: default “en”
- COUNTRY: default “us”
- Schedule the Script to run once a week. It is also fine to start it manually
- Use keyword_suggestions.csv for further analysis:
- first_seen: this is the date where the query appeared for the first time in the autosuggest
- last_seen: the date where the query was seen for the last time
- is_new: if first_seen == last_seen we set this to “True” – Just filter on this value to get the new trending searches in the google autosuggest
Here is the Python Code:
# Pemavor.com Autocomplete Trends
# Author: Stefan Neefischer (stefan.neefischer@gmail.com)
import concurrent.futures
from datetime import date
from datetime import datetime
import pandas as pd
import itertools
import requests
import string
import json
import time
charList = " " + string.ascii_lowercase + string.digits
def makeGoogleRequest(query):
# If you make requests too quickly, you may be blocked by google
time.sleep(WAIT_TIME)
URL="http://suggestqueries.google.com/complete/search"
PARAMS = {"client":"opera",
"hl":LANGUAGE,
"q":query,
"gl":COUNTRY}
response = requests.get(URL, params=PARAMS)
if response.status_code == 200:
try:
suggestedSearches = json.loads(response.content.decode('utf-8'))[1]
except:
suggestedSearches = json.loads(response.content.decode('latin-1'))[1]
return suggestedSearches
else:
return "ERR"
def getGoogleSuggests(keyword):
# err_count1 = 0
queryList = [keyword + " " + char for char in charList]
suggestions = []
for query in queryList:
suggestion = makeGoogleRequest(query)
if suggestion != 'ERR':
suggestions.append(suggestion)
# Remove empty suggestions
suggestions = set(itertools.chain(*suggestions))
if "" in suggestions:
suggestions.remove("")
return suggestions
def autocomplete(csv_fileName):
dateTimeObj = datetime.now().date()
#read your csv file that contain keywords that you want to send to google autocomplete
df = pd.read_csv(csv_fileName)
keywords = df.iloc[:,0].tolist()
resultList = []
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=MAX_WORKERS) as executor:
futuresGoogle = {executor.submit(getGoogleSuggests, keyword): keyword for keyword in keywords}
for future in concurrent.futures.as_completed(futuresGoogle):
key = futuresGoogle[future]
for suggestion in future.result():
resultList.append([key, suggestion])
# Convert the results to a dataframe
suggestion_new = pd.DataFrame(resultList, columns=['Keyword','Suggestion'])
del resultList
#if we have old results read them
try:
suggestion_df=pd.read_csv("keyword_suggestions.csv")
except:
suggestion_df=pd.DataFrame(columns=['first_seen','last_seen','Keyword','Suggestion'])
suggestionCommon_list=[]
suggestionNew_list=[]
for keyword in suggestion_new["Keyword"].unique():
new_df=suggestion_new[suggestion_new["Keyword"]==keyword]
old_df=suggestion_df[suggestion_df["Keyword"]==keyword]
newSuggestion=set(new_df["Suggestion"].to_list())
oldSuggestion=set(old_df["Suggestion"].to_list())
commonSuggestion=list(newSuggestion & oldSuggestion)
new_Suggestion=list(newSuggestion - oldSuggestion)
for suggest in commonSuggestion:
suggestionCommon_list.append([dateTimeObj,keyword,suggest])
for suggest in new_Suggestion:
suggestionNew_list.append([dateTimeObj,dateTimeObj,keyword,suggest])
#new keywords
newSuggestion_df = pd.DataFrame(suggestionNew_list, columns=['first_seen','last_seen','Keyword','Suggestion'])
#shared keywords with date update
commonSuggestion_df = pd.DataFrame(suggestionCommon_list, columns=['last_seen','Keyword','Suggestion'])
merge=pd.merge(suggestion_df, commonSuggestion_df, left_on=["Suggestion"], right_on=["Suggestion"], how='left')
merge = merge.rename(columns={'last_seen_y': 'last_seen',"Keyword_x":"Keyword"})
merge["last_seen"].fillna(merge["last_seen_x"], inplace=True)
del merge["last_seen_x"]
del merge["Keyword_y"]
#merge old results with new results
frames = [merge, newSuggestion_df]
keywords_df = pd.concat(frames, ignore_index=True, sort=False)
# Save dataframe as a CSV file
keywords_df['first_seen'] = pd.to_datetime(keywords_df['first_seen'])
keywords_df = keywords_df.sort_values(by=['first_seen','Keyword'], ascending=[False,False])
keywords_df['first_seen']= pd.to_datetime(keywords_df['first_seen'])
keywords_df['last_seen']= pd.to_datetime(keywords_df['last_seen'])
keywords_df['is_new'] = (keywords_df['first_seen']== keywords_df['last_seen'])
keywords_df=keywords_df[['first_seen','last_seen','Keyword','Suggestion','is_new']]
keywords_df.to_csv('keyword_suggestions.csv', index=False)
# If you use more than 50 seed keywords you should slow down your requests - otherwise google is blocking the script
# If you have thousands of seed keywords use e.g. WAIT_TIME = 1 and MAX_WORKERS = 5
WAIT_TIME = 0.2
MAX_WORKERS = 20
# set the autocomplete language
LANGUAGE = "en"
# set the autocomplete country code - DE, US, TR, GR, etc..
COUNTRY="US"
# Keyword_seed csv file name. One column csv file.
#csv_fileName="keyword_seeds.csv"
CSV_FILE_NAME="keywords.csv"
autocomplete(CSV_FILE_NAME)
#The result will save in keyword_suggestions.csv csv file